Media Over QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) is an experimental transport layer protocol developed by Google to replace the traditional TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and increase web page load speed. Understanding Media Over QUIC involves understanding how it impacts the performance, reliability, and security of online media content delivery.
One of the key insights about QUIC is that it reduces latency. It achieves this by establishing a connection with a single handshake, contrary to the TCP that requires multiple handshakes. This feature makes QUIC a more efficient protocol for streaming media, as it helps to reduce the delays often experienced when loading media content on web pages.
Another fundamental aspect of QUIC is its built-in encryption. This protocol, unlike TCP, comes with built-in TLS (Transport Layer Security) encryption, which makes it more secure. This feature is particularly crucial in the era of increased cybersecurity threats, as it helps to ensure that the media content delivered over the internet is secure from potential security breaches.
Regarding reliability, QUIC handles packet loss better than TCP. In TCP, if a packet is lost, the rest of the packets have to wait until the lost packet is retransmitted, which is known as head-of-line blocking. However, QUIC avoids this problem by giving each stream its own sequence of packet numbers, which allows for independent retransmissions. This feature makes QUIC more reliable for streaming media, as it ensures that the delivery of media content is not significantly affected by packet loss.
In terms of congestion control, QUIC also performs better than TCP. It has a more sophisticated congestion control mechanism that adjusts the rate of data transfer based on the network conditions. This feature helps to prevent network congestion, which can negatively impact the quality of streamed media content.
Moreover, QUIC is designed to work well with HTTP/2 and HTTP/3, the latest versions of the HTTP protocol. This means that it can take advantage of the performance improvements offered by these protocols, such as multiplexing and header compression, to deliver media content more efficiently.
However, despite these benefits, QUIC also has some challenges. One of them is the lack of support from some internet service providers and network devices, which can limit its effectiveness. Another challenge is the increased processing overhead due to the use of encryption and the need for continuous updates to keep up with the evolving security threats.
In conclusion, understanding Media Over QUIC involves appreciating its benefits in terms of performance, reliability, and security, and being aware of its challenges. As the internet continues to evolve, protocols like QUIC will play a critical role in shaping the future of online media content delivery.
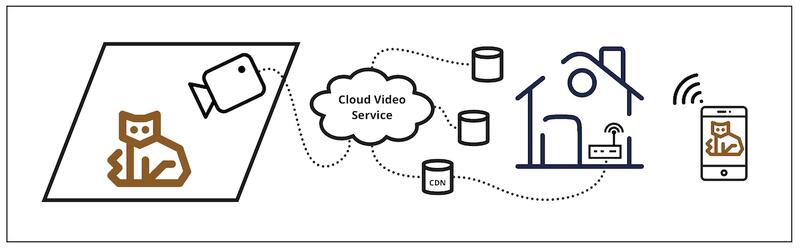
What Is Media Over QUIC?
Media Over QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) is a complex, yet innovative concept that has emerged in the digital sphere with the advent of high-speed internet. QUIC is a transport layer protocol developed by Google to improve the performance of web applications by reducing latency. When it comes to delivering media over QUIC, it primarily means transferring audio, video, and other forms of data over the QUIC protocol.
This protocol is designed to make the internet work faster by reducing the time it takes for data to travel back and forth between a client and server. Traditional protocols such as TCP/IP often face issues such as packet loss, latency, and blocking which affect the quality of media content being transferred over the network. QUIC, however, overcomes these obstacles by running a multitude of parallel streams over a single User Datagram Protocol (UDP) connection.
This allows it to recover from packet loss or latency much quicker than TCP/IP as it doesn’t interpret packet loss as congestion and react by slowing down. In essence, Media over QUIC has the potential to significantly enhance the quality and speed of media streaming and data transfer in the digital world. As the protocol continues to evolve and gain acceptance, it may well revolutionize the way we consume media online.

How Does Media Over QUIC Function?
Media Over QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) is a transport protocol that functions to enhance the speed and performance of media delivery over the internet. QUIC was developed by Google to optimize online browsing speed by reducing the time needed to establish a secure connection. It utilizes the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) instead of the traditional Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), which is one of the primary reasons behind its high-speed performance.
When it comes to media delivery, Media Over QUIC ensures a faster and more secure streaming experience. It does this by combining HTTP/2, TCP, TLS, and UDP into a single protocol powered by UDP. The combination of these protocols helps in overcoming the latency issues that are commonly associated with TCP-based transport, thereby enhancing the speed of media delivery.
Moreover, QUIC incorporates built-in encryption for data security, which is an upgrade from the traditional HTTP protocol that does not offer any encryption. This ensures the safe transmission of media content over the internet. Apart from security, QUIC is also designed to handle packet loss better than TCP, which can be beneficial in preventing buffering during media streaming.
Media Over QUIC functions by establishing multiple connections to a server. This allows it to send several streams of data simultaneously, resulting in a more efficient use of bandwidth and reducing congestion on the network. In addition, QUIC’s congestion control and loss recovery mechanism are more responsive than TCP, which further boosts its efficiency in media delivery.
In summary, Media Over QUIC functions as a more efficient, secure, and faster protocol for media delivery over the internet. Its use of UDP, built-in encryption, and multiple connections make it a promising solution for improving the online streaming experience. By reducing latency, handling packet loss effectively, and ensuring secure connections, QUIC is set to revolutionize the way media is delivered over the internet.
Additional Capabilities Enabled by Media Over QUIC
Media Over QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) has sparked a revolution in the world of internet communications, providing a multitude of additional capabilities that weren’t available before. QUIC is a transport protocol developed by Google, which combines the features of TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol), while also incorporating built-in encryption for secure communication. Implementing media over QUIC offers numerous advantages, particularly in terms of speed, security, and reliability.
One of the primary benefits of QUIC is its ability to reduce connection establishment time. In traditional TCP connections, there is a significant delay due to the round-trip time (RTT) needed to establish a secure connection. However, QUIC uses a zero-RTT connection establishment, which drastically reduces latency and improves the speed of media delivery.
Additionally, QUIC provides superior security compared to TCP or UDP, as it integrates encryption directly into the protocol. This ensures that the media being transmitted is secure from potential interception or manipulation. This built-in encryption can be particularly beneficial for media companies that transmit sensitive content, such as live broadcasts or premium content.
Finally, QUIC’s multiplexing feature enables multiple data streams to be sent over a single connection. This is a significant improvement over TCP, which requires a separate connection for each data stream. Multiplexing not only improves efficiency but also enhances the reliability of media delivery, since if one data stream encounters an issue, the others can continue without interruption.
In conclusion, the introduction of Media Over QUIC has enabled a range of additional capabilities that significantly enhance the speed, security, and reliability of internet communications. These improvements are particularly beneficial for media and entertainment companies, who can leverage these capabilities to deliver high-quality, secure content to their viewers.
Why Adopt Media Over QUIC Now?
Adopting Media over QUIC now is a strategic move that can bring about a remarkable transformation in web performance and user experience. QUIC, or Quick UDP Internet Connections, is a transport protocol developed by Google to enhance the web’s speed, reliability, and security. Media over QUIC offers a plethora of benefits that cater to the ever-evolving digital landscape. It not only reduces latency but also provides a secure and robust connection, making it an excellent choice for video streaming and other real-time applications.
The need for speed is of utmost importance in the digital world. Slow loading times can lead to user dissatisfaction, hence adopting Media over QUIC can significantly improve this aspect. Its ability to establish a connection with only a single round-trip time (RTT) instead of the traditional three RTTs used by TCP, ensures faster delivery of content. Moreover, it operates over UDP, which bypasses typical TCP bottlenecks, further enhancing speed and performance.
Security is another critical aspect that Media over QUIC addresses effectively. It employs encryption by default, which means that users can enjoy safer connections without the need for additional protocols. This aspect is particularly beneficial for businesses as it enhances customer trust and confidence.
Finally, Media over QUIC is designed to mitigate the common problem of head-of-line blocking, where a lost or delayed packet causes a delay in the entire data stream. It achieves this by allowing for independent transmission of streams, ensuring that a problem with one stream does not affect the others. This feature is particularly beneficial for applications that require simultaneous transmission of multiple data streams, such as video conferencing or multiplayer gaming.
In conclusion, adopting Media over QUIC now is a strategic move for businesses and developers alike, as it addresses key aspects of web performance and security while adapting to the ever-evolving digital landscape.

Current Status and Future Directions for Media Over QUIC
Media over QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) is an emerging area of interest in the media industry. Currently, the status of media over QUIC is still in its infancy, with the protocol itself only being finalized by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) in 2018. However, there is a significant amount of research and development ongoing to explore the potential benefits and challenges of this new approach. QUIC aims to provide improved performance over traditional transmission protocols, particularly in conditions of high latency or packet loss, which could potentially revolutionize the delivery of media content over the internet.
Looking forward, the future directions for media over QUIC are promising. The protocol’s ability to minimize latency, maintain connection integrity, and deliver high-quality media is expected to spur its adoption in the coming years. Particularly in the realm of live streaming and interactive media, where latency and connection stability are crucial, QUIC has significant potential to improve user experiences.
Efforts are underway to make QUIC compatible with HTTP/3, the forthcoming version of the HTTP protocol, which would integrate QUIC’s benefits into the backbone of the internet. This could pave the way for broader use of QUIC in media delivery, as it would enable seamless integration with existing web services and technologies.
The development of QUIC also represents a shift towards more use of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) in the media industry, as opposed to the traditionally dominant Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). This is in response to the increasing demands of modern media applications, which require lower latency and more efficient data transmission.
However, there are still challenges to be addressed, including the need for widespread support and adoption by browsers and operating systems, as well as ensuring compatibility with existing network infrastructure. It is also crucial to address any potential security issues associated with the use of QUIC. Despite these challenges, the future of media over QUIC is bright, with the potential to significantly enhance the delivery and consumption of media content on the internet.
